Which nematode causes ear cockle disease of wheat?
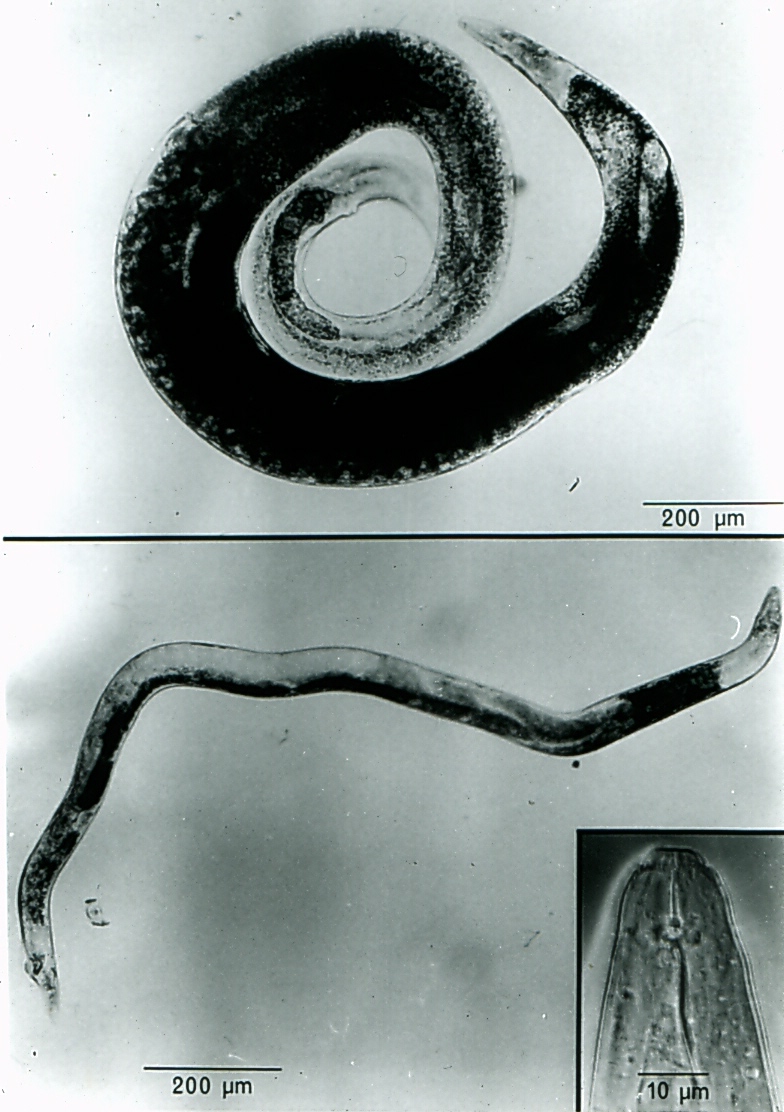
Anguina tritici, commonly referred to as wheat seed gall nematode, is the cause of ear-cockle disease. It was the first plant-parasitic nematode to be described in the scientific literature in 1743.
What are seed gall nematodes?
Anguina tritici was the first plant parasitic nematode to be described in the literature in 1743. It causes a disease in wheat and rye called “ear-cockle” or seed gall. Originally found in many parts of the world but has been eradicated from the western hemisphere. Currently in north Africa and west Asia only.
What is Molya disease?
2) Cereal cyst nematode causes “Molya disease” in wheat and barley. Second stage juvenile (J2) is the infective stage which enters inside the plant and start feeding on permanent feeding site known as “Syncytium” which acts as a metabolic sink.
What causes black point in wheat?
Black point is a disease that affects wheat and barley; it is most important on durum wheat. It is caused by several common fungi. These fungi are most troublesome when the relative humidity exceeds 90%. Expanding green kernels are most susceptible, while premature seed senescence also promotes black point.
How do you control powdery mildew in wheat?
Incorporating wheat residues into the soil, destroying volunteer wheat and crop rotation will reduce the amount of overwintering inoculum in the field. Fungicides are available that provide excellent control of powdery mildew.
How does crop rotation help plant disease management?
The goal of crop rotation is to reduce the amount of the pest population present in the soil. Some pathogens that cause diseases survive in the soil from year to year in one form or the other, usually as sclerotia, spores, or hyphae. Rotating to non-host crops prevents the buildup of large populations of pathogens.
What are the diseases caused by nematodes in plants?
Some of the most damaging nematodes are: Root knot (Meloidogyne spp.); Cyst (Heterodera and Globodera spp.); Root lesion (Pratylenchus spp.); Spiral (Helicotylenchus spp.); Burrowing (Radopholus similis); Bulb and stem (Ditylenchus dipsaci); Reniform (Rotylenchulus reniformis); Dagger (Xiphinema spp.); Bud and leaf ( …
What is the treatment for nematodes?
The treatment of choice for intestinal nematodes, with the exception of Strongyloides, is albendazole or mebendazole. Single-dose or short-course regimens with these oral agents (albendazole 400mg once or mebendazole 500mg once, or 100mg BID for 3 days) cure more than 90% of Ascaris infections.
How do nematicides work?
When systemic nematicides are applied to moist soil, the active ingredients are rapidly released (even from granules) and absorbed by plant roots. For Temik, movement in plants is bidirectional, both up and down. When they are applied to soil, the toxicant is moved upward to the foliar parts of the plant.
How seed galls can be removed from seed lots of wheat?
The most effective control is by mechanical seed cleaning. Galls may be also removed by submersion of the seed in 20% brine solution (galls float to the surface), followed by thorough washing in water. Hot water treatment at 54°C for 10 min is also reported to be effective in killing the nematodes.
Which chemical is used to control nematodes?
Nematicides are a type of chemical pesticide that is used to kill nematodes, microscopic parasitic worms that can live in soil or water.
What is the largest intestinal nematode?
Ascaris lumbricoides is the largest and most common intestinal nematode of humans. Females are approximately 30 cm long; sexually mature males are smaller. The diameter varies from 2 to 6 mm.
Who discovered Anguina tritici for the first time?
Needham in 1743 – that is, wheat seed gall nematode Anguina tritici (Steinbuch, 1799; Filipjev, 1936) [2].
Which physical method is useful for nematode management?
Heat: Heat treatment is probably the most successful physical control measure developed so far. It is widely used for the killing of nematodes within plant tissues before planting and has proved useful on nematode infested bulbs and tubers, and roots of plants such as chrysanthemums, strawberries, bananas and citrus.
Which one is first reported plant nematode?
First Report of Plant-Parasitic Nematode Meloidoderita salina in the Netherlands.
Which is the smallest plant parasitic nematode?
Pin Nematodes (Paratylenchus spp.) are the smallest plant parasitic nematodes that attack plants. Adult females found in mint average 0.4 mm (0.016 inch). Another pin nematode (Gracilacus spp.) is occasionally found in mint but only differs from Paratylenchus in that it has a much longer stylet.
Which nematode is Ovoviviparous?
Ovoviviparous nematodes include threadworms and hookworms because they lay eggs with larvae. Viviparous nematodes are Trichinella spiralis , filarial worms and Dracunculus medinensis (Guinea worm) because they give rise directly to larvae [5, 6, 7].
Who is father of Indian nematology?
N.A. Cobb, the father of nematology.
Who is the father of Nematology?
Nathan Augustus Cobb, referred to as the “Father of Nematology in the United States” (56), was a Renaissance man and a man of humble beginnings.
Who identified first nematode in India?
The golden cyst nematode, Globodera rostochiensis (Woll.) Behr., was first discovered by Jones (1961) and since then both G.
Who is father of Indian plant pathology?
Sir Edwin John Butler is known as the father of modern plant pathology in India.
Who described the first plant nematode disease in 1743?
Turbevil Needham (1743) accidently recorded first plant parasitic nematode when he crushed one of the shrunken and blackened wheat grains and observed “Aquatic worms, Eels, or Serpents, which they very much resemble.” He named it Vibrio tritici. Later this nematode was rightly named as Anguina tritici by Steinbuch.
Which nematicides group are non fumigant in nature?
Summary. Non-fumigant nematicides available for vegetable production in Florida include two broad categories, chemical nematicides and biological nematicides. Chemical nematicides can be divided into three pesticide classes: carbamates, organophosphates, and 3-fluorine nematicides.
WHO classified nematodes?
Nematode systematics
An early and influential classification was proposed by Chitwood and Chitwood—later revised by Chitwood—who divided the phylum into two classes—Aphasmidia and Phasmidia.
Which disease is caused by nematodes?
Nematode infections in humans include ascariasis, trichuriasis, hookworm, enterobiasis, strongyloidiasis, filariasis, trichinosis, dirofilariasis, and angiostrongyliasis (rat lungworm disease), among others.
What are 5 characteristics of nematodes?
- Their body is bilaterally symmetrical and triploblastic.
- They are cylindrical in shape.
- They exhibit tissue level organization.
- Their body has a cavity or pseudocoelom.
- The alimentary canal is distinct, with the mouth and the anus.
- They are sexually dimorphic.
WHO reported root-knot nematode?
Root-knot nematodes were first reported in 1855 by Berkeley, who observed them causing damage on cucumbers. Until Chitwood’s work in 1949, which defined 4 species and one subspecies (M. incognita acrita) within the genus Meloidogyne, the root-knot nematodes were all considered the same species, Heterodera radicola.
What is soil nematode?
Soil nematodes are very small (0.3–5.0 mm long as adults) worm-like animals which are very abundant (commonly millions m− 2) and diverse (commonly > 30 taxa) in all soils (Yeates, 1979).
What is plant parasitic nematode?
Nematodes are thread-like roundworms that live in a wide range of environments including soil and fresh and salt water. … Nematodes that feed on plant parts are called plant parasitic nematodes (PPN) and are ubiquitous in agricultural soils.
What is fumigant and nematicide?
Nematicides can be divided into two categories: fumigants and nonfumigants. Fumigants are broad-spectrum pesticides where the active ingredient moves through the soil as a gas. Fumigants are not taken up by plants or bound by soil, so they do not have a long period of residual pesticidal activity.
WHO reported first plant parasitic nematode?
The first described plant parasitic nematodes were discovered in wheat seeds by Needham (1743).
Why are plant parasitic nematodes important?
Free- living nematodes are very important in maintaining the soil bio-dynamic system, especially in soil with low organic matter content, whereas PPNs feed on plants and reduce crop growth and yield efficiency.
Which of the following is a nematicide?
A nematicide is a type of chemical pesticide used to kill plant-parasitic nematodes. … Aldicarb (Temik), a carbamate insecticide marketed by Bayer CropScience, is an example of a commonly used commercial nematicide. It is important in potato production, where it has been used for control of soil-borne nematodes.
In what order most of the plant parasitic nematode belong?
All plant parasitic nematodes (Fig. 15-3) belong to the phylum Nematoda. Most of the important parasitic genera belong to the order Tylenchida, but a few belong to the order Dorylaimida. Ditylenchus, stem or bulb nematode of alfalfa, onion, narcissus, etc.
What are the examples of nematicides?
| Crop | Nematode pest | Nematicide |
|---|---|---|
| Tomato, cucurbits | Meloidogyne spp. | Fenamiphos |
| Dazomet | ||
| Citrus | Tylenchulus semipenetrans | Fenamiphos |
| Aldicarb |
How do I get rid of nematodes in my soil?
To kill nematodes in soil, heat small quantities of moist soil to 140°F in the oven or by solarization. Heating soil in the oven over a time period needed to bake a medium-sized potato placed in the center of the soil is sufficient to kill nematodes; however, this is only practical for small quantities of soil.
How can nematodes be prevented?
Prevent nematodes from entering your garden by using only nematode-free plants purchased from reliable nurseries. To prevent the spread of nematodes, avoid moving plants and soil from infested parts of the garden. Don’t allow irrigation water from around infested plants to run off, as this also spreads nematodes.
How do I know if I have nematodes?
Typical symptoms of nematode damage can appear above and below the ground in foliage and roots. Foliar symptoms generally appear in the form of stunting of plants, premature wilting, and leaf chlorosis (yellowing). … Root symptoms caused by sting or root-knot nematodes can present very noticeable symptoms.