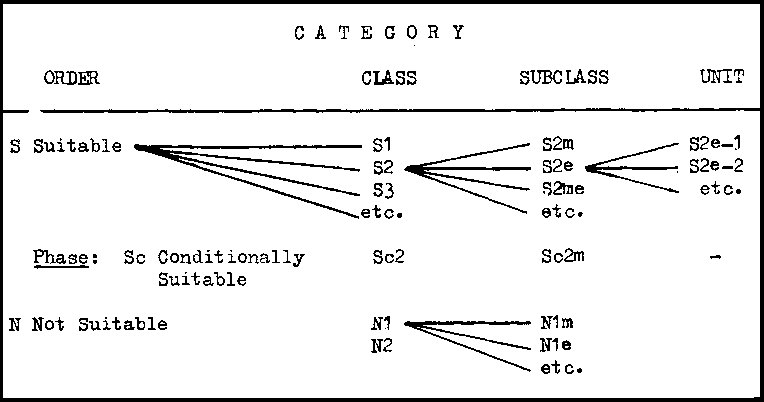
What are the land suitability classes?
Land suitability Classes reflect degrees of suitability. The classes are numbered consecutively, by arabic numbers, in sequence of decreasing degrees of suitability within the Order. Within the Order Suitable the number of classes is not specified. There might, for example, be only two, S1 and S2.
What are the 8 Land Capability Classes?
Land capability class definitions area as follows: Class I contains soils having few limitations for cultivation; Class II contains soils having some limitations for cultivation; Class III contains soils having severe limitations for cultivation; Class IV contains soils having very severe limitations for cultivation; …
In which class land is suitable for agriculture?
Five classes of agricultural land were proposed; namely, Agriculture Class I, II, III, IV, and V. Agriculture Class I represents the best area and is the most suitable for agriculture. In contrast, Agriculture Class V is not suitable for agriculture.
What are the four types of land use?
- Functional zoning. The most prevalent form of zoning where land use zones are defined according to their function, such as commercial, residential, or industrial. …
- Form-based zoning. …
- Intensity zoning. …
- Incentive zoning.
What is soil class 3rd?
Soil is mainly made up of gravel , sand , clay , humus, water and air. Q 2. … The rotted remains of dead plants and animals is called humus. Humus helps plants to grow well. Q 3.
What is Class C soil?
Type C is the least stable soil. … Type C soil is the least stable type of soil. Type C includes granular soils in which particles don’t stick together and cohesive soils with a low unconfined compressive strength; 0.5 tons per square foot or less. Examples of Type C soil include gravel, and sand.
What are the 7 factors that determine land capability class land use?
Use for cultivated crops is limited as a result of the effects of one or more permanent features such as (1) steep slopes, (2) severe susceptibility to water or wind erosion, (3) severe effects of past erosion, (4) shallow soils, (5) low moisture-holding capacity, (6) frequent overflows accompanied by severe crop …
What is soil class 7th?
The mixture of rock particles and humus is called the soil. Living organisms, such as bacteria, plant roots and earthworm are also important parts of any soil. The soil is classified on the basis of the proportion of particles of various sizes.
What are the five types of land use define these uses?
There are five main different types of land use: residential, agricultural, recreation, transportation, and commercial. Managing the various uses of land occurs through partnerships between state, federal, and municipal entities, but many decisions affecting local projects occur at the municipal level.
What are the 3 types of land?
- Residential. As the name suggests, residential land is a type of real estate that is meant to be used for private housing. …
- Commercial Land. …
- Industrial Land.
How is land capability and suitability classification important for watershed planning?
This land capability classification should ensure appropriate land use for every land area for peaceful coexistence of different flora and fauna including human habitation and also a sustained productivity through human activities.
What is the difference between suitability and capability?
Capability: The ability to do new things! Suitability: The ability to do things well.
How is land capability classified?
The land capability classification is grouped into three major categories of soil viz. i) Capability unit ii) Capability sub class and iii) capability class. … The third broadest category of land capability is a group of soils having the same degree of limitations.
What is a Class 6 soil?
Class 6 soils have severe limitations that make them generally. unsuitable for cultivation and that restrict their use mainly to. pasture, etc.
What are the types of suitability?
The rule, moreover, identifies the three main suitability obligations: reasonable-basis, customer-specific, and quantitative suitability.
What is the difference between land capability and land suitability?
Land Capability is closer to the ecology. … Land Suitability is less closer to the ecology. 4. It recognizes the consequences of altering other structure or process.
What are the three elements of an appropriate suitability assessment?
05 Components of Suitability Obligations. Rule 2111 is composed of three main obligations: reasonable-basis suitability, customer-specific suitability, and quantitative suitability.
What is suitability standard?
The suitability standard requires only that investments be suitable to the investor’s circumstances, and may allow a broker to recommend an investment that is more costly and generates a higher commission than a similar low-priced option.
How do you determine suitability?
- Age.
- Investment goals.
- Investment timeframe.
- Risk tolerance.
- Financial situation and obligations.
- Liquidity needs.
- Current investment portfolio and assets.
- Investment knowledge, sophistication, and experience.
What is suitability map?
Often, the result of a suitability analysis is a suitability map. It shows which locations or areas are suitable for a specific use in form of a thematic map (e.g. agricultural suitability map). … It segregates areas that are exposed to a specific hazard based on the criteria given (e.g. avalanche hazard maps).
What is a suitability map GIS?
Site selection or suitability analysis is a type of analysis used in GIS to determine the best place or site for something. Potential sites used in suitability analysis can include the location of a new hospital, store or school among many others.
What is land suitability analysis?
Land Suitability Analysis (LSA) is a GIS-based process applied to determine the suitability of a specific area for considered use, i. e. it reveals the suitability of an area regarding its intrinsic characteristics (suitable or unsuitable).
What is a suitability score?
The Suitability Score is a numerical value indicating a location’s overall suitability for a given land use when all of the suitability factors are considered.
What is the purpose of site suitability analysis quizlet?
Site suitability is the process of selecting the best location for a particular purpose based on specified criteria. Criteria may have any number from one to hundreds.
How do you conduct a suitability analysis?
- Open the Make Suitability Analysis Layer tool.
- From Input Features, you have the option to select a feature layer from your project or browse for hosted or shared content. Click the browse button. …
- Type Market Suitability Candidates in the Layer Name text box.
- Click Run.
How do you make a habitat suitability model?
- Determine and prepare the criteria data.
- Transform the values of each criterion to a common suitability scale.
- Weight criteria relative to one another and combine them to create a suitability map.
- Locate the areas for the siting or to preserve.
How is land classified on the basis of land use?
They were: (i) Forest (ii) Area not available for cultivation (iii) Other uncultivated land excluding current fallows Page 2 (iv) Fallow land and (iv) Net area sown. This fivefold classification was merely a broad outline of land use in the country.
How does weighted overlay work?
Using the Weighted Overlay tool
Reclassifies values in the input rasters into a common evaluation scale of suitability or preference, risk, or some similarly unifying scale. Multiplies the cell values of each input raster by the rasters’ weight of importance.
Which one is lower category for classification of soil?
The soil series is the lowest category in the soil classification system.
How many categories or level of classification are there in the structure of soil suitability classification?
These four classes are differentiated based on the extent of soil slope, erosion, depth, structure, soil reaction and drainage.
Which of the following land suitability class is suitable for aesthetic purposes?
Class VIII:
These lands should be used only for recreation, wildlife, water supply or aesthetic purposes.
Which land is suitable for agriculture class 8?
Agricultural activities are concentrated in those areas of the world which have suitable conditions of growing crops. What is arable land? Answer: The land on which crops are grown is called arable land.
What is a Class 1 land?
Class I (1) soils have slight limitations that restrict their use. Class II (2) soils have moderate limitations that reduce the choice of plants or require moderate conservation practices. Class III (3) soils have severe limitations that reduce the choice of plants or require special conservation practices, or both.
What are the 5 types of land?
Types of land uses. There are many different categories when it comes to land use. The five most common uses are recreational, transport, agricultural, residential and commercial.
What are the 6 types of land?
Types of Land Use
Those types include recreational, transport, agricultural, residential, and commercial.