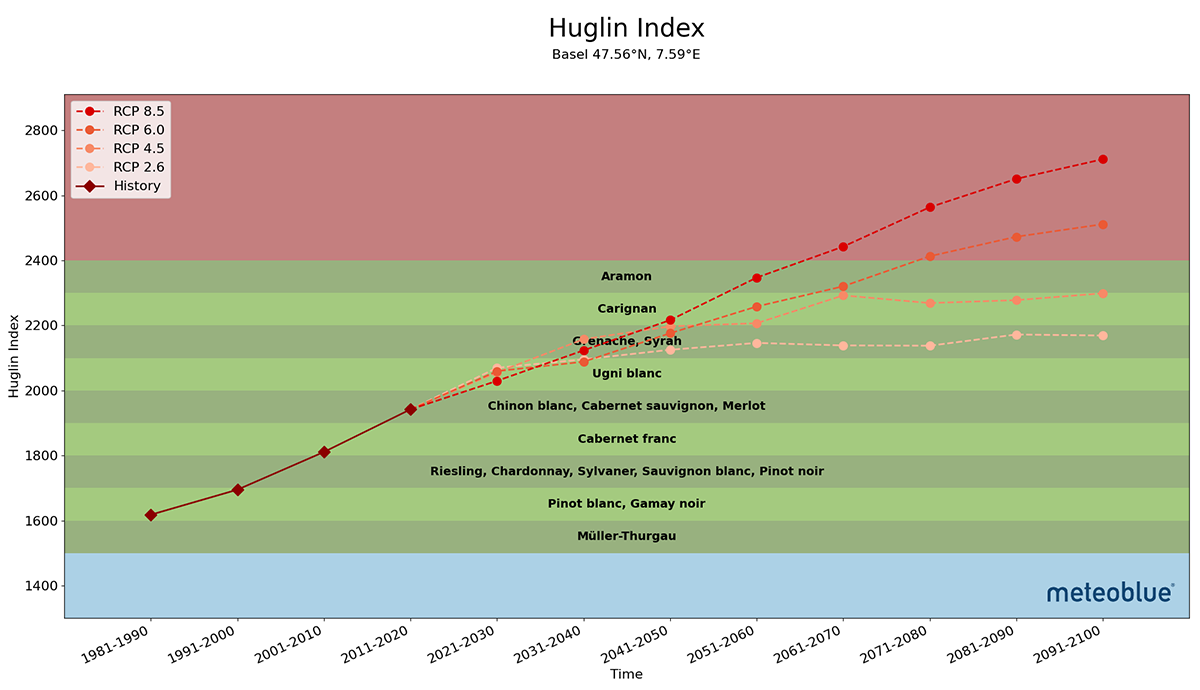
How to calculate Huglin index?
The Huglin Index was determined by summing the mean and maximum temperatures above 10 ◦C for the period from 1 April to 30 September. This calculation took into account a coefficient associated with the length of day “d”, which ranges between 1.02 and 1.06 in latitudes between 40◦ and 50◦ [37].
How do you calculate growing degree days for grapes?
GDD = (Tmax + Tmin) / 2 – Tbase
Base temperature for grapevines is usually set to 10°C but it can be more depending on the growing region. Also, each grapevine pest has its own base temperature that is required for them to develop.
How do you calculate growing degree days for wine?
It is calculated by taking the average temperature for each month of the seven month growing season (October to April in the Southern Hemisphere, and April to September in the Northern Hemisphere), divided by seven.
What is radiation use efficiency?
Radiation-use efficiency is defined as the ratio of dry matter. produced per unit of radiant energy used in its production. (Monteith 1977).
What is GDU in farming?
Growing Degree Units (GDU) is a measurement of the amount of heat needed for a corn plant to reach various stages such as tassel or maturity. … Your GDUs will help determine when fields will be ready for harvest.
How do you calculate growing degree days for turf?
Growing degree days are calculated by averaging the daily maximum and minimum temperatures and comparing it to a base temperature. This formula subtracts the base temperature from the average daily temperature and calculates the number of heat units for that day or GDDs.
How do you use growing degree days?
If the mean temperature is at or below TBASE, then the Growing Degree Day value is zero. If the mean temperature is above TBASE, then the Growing Degree Day amount equals the mean temperature minus TBASE. For example, if the mean temperature was 75° F, then the GDD amount equals 10 for a TBASE of 65° F.
How do you calculate growing degree days for wheat?
Growing degree days GDD (°F or °C) for wheat accumulated daily from the planting date to the end date. Calculated from: ((Daily Max Temp + Daily Min Temp)/2) – 32 °F (or ((Daily Max Temp + Daily Min Temp)/2)). If daily Max or Min Temp < 32 °F (0 °C) it’s set equal to 32 °F (0 °C).
Why Is Growing Degree Days important?
The importance of GDD is that those numbers can help researchers and growers predict when an insect enters a certain stage of development and aid in control. Likewise, for crops, the GDD can help growers predict growth stages such as flowering or maturity, make seasonal comparisons, etc.
What is heat summation wine?
wine-making process
amount of heat, called the heat summation, is calculated by totaling the number of degrees of average daily temperature over 10 °C for each day of the growing season. A heat summation of about 1,800° is required for successful growth.
What are growing degree hours?
In short, Growing Degree Hours (GDH) are a measure of heat accumulation that we use to predict plant development. It is calculated as a cumulative sum of hourly temperature above a threshold for each hour of the day, excluding high temperatures that cause plant stress.
Can Growing Degree Days be negative?
Growing degree days can vary only from 0 to 36. You cannot have negative growing degree days.
What is photothermal unit?
The photothermal unit concept provides a reliable index for the progress of the crop that can be used to predict the yield of any crop. Therefore present investigation was undertaken to study the thermal effect on growth and yield of wheat under different sowing environments.
What is a degree day wine?
The Winkler scale, which has become the most widely used method of classifying wine growing regions all around the world, was based upon the concept of “degree-days” – calculated by the amount that each day’s average temperature exceeds 50° Fahrenheit, between the growing season months of April and October.
What is Helio thermal unit?
Helio-thermal units (HTU): The HTU may be defined as the accumulated product of. GDD and bright sunshine hours between the developmental. thresholds for each day.
How do you calculate growing degree units?
Growing Degree Units (GDUs)
GDD or GDU = (Daily Maximum Air Temperature + Daily Minimum Temperature)/2 – 50.
What is the temperature of universe?
The average temperature of the universe today is approximately 2.73 kelvins (−454.76 °F), based on measurements of cosmic microwave background radiation.
Is Cardinal a temperature?
The minimum cardinal temperature is the lowest temperature at which crop growth can occur; this temperature is referred to as the base temperature, and no growth occurs below this temperature. The optimum cardinal temperature is the temperature at which crop growth and performance are at their maximum.
What Are Growing Degree Days viticulture?
The progression of in-season grapevine development is strongly influenced by air temperature. As such, average heat accumulation is often used to compare regions and vine growing condition. This average heat accumulation is often referred to as Growing Degree Days (GDD).
How many days does a tomato plant need to grow?
A Growing Degree day is calculated by adding the low temperature of a day to the high temperature of the day and dividing by 2. From the result, 50 is subtracted… because most plants don’t grow at temperatures below 50 degrees. Tomatoes need somewhere above 1300 GDD to ripen.
What is photothermal quotient?
The photothermal ratio (PTR), also named photothermal quotient, is a variable that characterizes the amount of light available to plants relative to the temperature level. It is used in plant biology to characterize the growth environment of plants.
How do you calculate a photothermal unit?
Photo-thermal unit (PTU) (degree-days hours) was calculated on the basis of GDD and day length with the formula given below: (Eruola et al ., 2014)PTU= GDD x Day length Halio-thermal unit (HTU) (degree-days hours) was calculated on the basis of GDD and sunshine hours by the following formula: (Eruola et al ., 2014)HTU …
What is heat use efficiency?
The heat use efficiency (HUE) indicated capacity of the plant to harvest dry matter per unit of heat use. The HUE was computed at different phonological stages of three pea cultivars under different environment (D1 and D2) and two row orientations were given in Table 3.
How do you calculate heat efficiency?
Helio thermal use efficiency was calculated by dividing the total dry matter recorded at respective days by the accumulated helio thermal units and expressed as g oC days-1 hrs-1.