What causes swine vesicular disease?
Swine vesicular disease is a viral vesicular disease of pigs caused by an enterovirus closely related to human coxsackie virus B5. It is generally a mild disease that was endemic in Italy until recently; it has occurred only sporadically in other countries.
What is vesicular disease in animals?
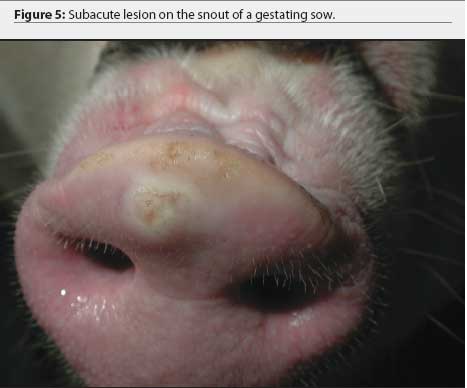
Vesicular stomatitis (VS) is a viral disease of livestock transmitted primarily by biting flies and midges. The disease results in characteristic vesicular lesions that can occur on the muzzle, lips, tongue, ears, sheath, udder, ventral abdomen, and/or coronary bands.
Can humans get vesicular stomatitis?
Humans can contract vesicular stomatitis by coming into contact with lesions, saliva, or nasal secretions from infected animals. In people, the disease causes an acute influenza- like illness with symptoms such as fever, muscle aches, headache, and malaise.
Can humans get vesicular exanthema?
Vesicular exanthema of swine virus (VESV) is a virus which produces a disease in pigs that is clinically indistinguishable from the viruses causing foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) and swine vesicular disease (SVD). VESV affects only pigs and marine mammals. It is not transmissible to humans.
What is stomatitis caused by?
Often it will be due to injury, infection, allergy, or skin disease. Share on Pinterest Biting the inside of the cheek or lip can cause stomatitis to occur. The most common causes are: trauma from ill-fitting dentures or braces, biting the inside of the cheek, tongue, or lip, and surgery.
What states have vesicular stomatitis?
Vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV), a reportable animal disease, has been found in seven states in 2020: Arizona, Kansas, Missouri, Nebraska, New Mexico, Oklahoma and Texas. As VSV may spread throughout the Midwest and mountain states, livestock owners, especially those with horses, should be looking for symptoms.
Can VSV infect humans?
Yes. Humans can become infected with VSV when handling infected ani- mals (direct contact). In affected people, vesicular sto- matitis causes a flu-like illness with symptoms of fever, muscle aches, headache and weakness. Rarely, humans can get oral blisters similar to cold sores.
What type of virus causes rabies?
Rabies is caused by a lyssavirus (a form of virus that causes encephalitis) that affects the saliva and nervous system. Most cases of rabies in humans are caused by a bite or scratch from an infected animal.
What does strangles do to horses?
It affects horses, donkeys and ponies of all ages, breed and sex. The bacteria often infect the lymph nodes around the jaw, causing them to become swollen. In severe cases they can become so swollen that horses struggle to breathe properly, hence the name ‘Strangles’.
What are the symptoms of vesicular stomatitis?
Vesicular stomatitis in humans tends to cause severe flu-like symptoms such as headache, fever, muscle aches, and extreme fatigue. People rarely develop blisters in their mouths. However, if you experience influenza-like symptoms after working with a VS-infected horse, contact your physician immediately.
Is vesicular stomatitis in horses reportable?
“Vesicular stomatitis is a reportable disease; state and federal animal health authorities will be contacted by a horse owner’s local veterinarian and the state veterinarian will quarantine an affected farm or ranch if a case is confirmed through testing,” he said.
What does it mean when a horse’s tongue hangs out?
If you see a horse sticking out his tongue and chewing on it when he’s just standing in his stall, he has learned this behavior and has almost become addicted to the feeling. Saddle fit or back pain may also cause the horse to seek a way to find an endorphin release.
Is swine vesicular disease in the US?
| Swine vesicular disease virus | |
|---|---|
| Virus classification | |
| Order: | Picornavirales |
| Family: | Picornaviridae |
| Genus: | Enterovirus |
What virus causes vesicular stomatitis in horses?
Causes of Vesicular Stomatitis in Horses
In the western hemisphere, the Indiana serotype and New Jersey serotype are the two of interest. These viruses are similar in size and morphology but cause the animal to develop differing antibodies if affected.
Can humans get diseases from pigs?
Most commonly, human infections with variant viruses occur in people with exposure to infected pigs (e.g., at a fair or at work). Illness associated with variant virus infection includes symptoms similar to those of seasonal flu. Most illness has been mild, but as with seasonal flu, hospitalization and death can occur.
Which of the following vesicular diseases that can affect swine is currently found in the US?
Vesicular Exanthema of Swine (VES). Vesicular stomatitis caused by strains of vesicular stomatitis virus serotype New Jersey and subtype Indiana 1 is the only vesicular disease currently found in the United States.
What are the most common pig diseases?
- 1 Exudative dermatitis (greasy pig) …
- 2 Coccidiosis. …
- 3 Respiratory diseases. …
- 4 Swine dysentery. …
- 5 Mastitis. …
- 6 Porcine parvovirus.
What are the common diseases of swine?
- Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome virus (PRRSv) …
- Enzootic pneumonia (Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae) …
- Pleuropneumonia (Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae) …
- Swine dysentery (Brachyspira hyodysenteriae) …
- Meningitis (Streptococcus suis)
How do pigs get swine dysentery?
The disease is transmitted from carrier pigs (including farrowing sows) who excrete the organism in the feces for a long time. Mechanical transmission through infected feces in equipment, feed distribution contaminated trucks, boots and birds. May be transmitted through flies, mice, birds and dogs.
Can humans get swine dysentery?
Brachyspira innocens which is considered non-pathogenic. Brachyspira pilosicoli which is often associated with a less severe colitis and may also cause disease in chickens and humans.
Can you survive dysentery?
If left untreated, dysentery can lead to severe dehydration and become life-threatening.
Is vesicular exanthema reportable?
Suspected cases of vesicular exanthema should be reported immediately to the appropriate authorities.
Can pigs get cholera?
Classical swine fever (CSF), also known as hog cholera, is a contagious viral disease of domestic and wild swine. It is caused by a virus of the genus Pestivirus of the family Flaviviridae. The most common method of transmission is through direct contact between healthy swine and those infected with CSF virus.
What does swine dysentery look like?
Clinical Presentation. The typical pig affected with swine dysentery will appear dull, depressed and inappetant with sunken (or slab) sides to its abdomen. Dehydration is common. The faeces will range from soft to almost water, containing blood, mucous and in severe cases necrotic gut lining.
Is vesicular exanthema zoonotic?
Vesicular Stomatitis. Vesicular stomatitis is a reportable and zoonotic disease which is indistinguishable clinically from foot and mouth disease as well as other vesicular diseases.
What are signs of hog cholera?
Four days to three weeks after exposure, the disease begins with fever. Subsequent signs vary somewhat: loss of appetite, general depression and withdrawal from other animals, reddened and draining eyes, vomiting, constipation or diarrhea, and coughing and difficulty in respiration.
What is bovine stomatitis?
Bovine papular stomatitis is a disease caused by Bovine papular stomatitis virus, of the family Poxviridae and the genus Parapoxvirus. It occurs worldwide in cattle. Symptoms include reddish, raised, sometimes ulcerative lesions on the lips, muzzle, and in the mouth. It usually occurs before the age of two years.
What is the treatment for hog cholera?
There are no treatments for CSFV. Instead, vaccination against CSFV is used to prevent the disease and is usually applied in regions of the world where CSF is endemic. Countries considered free of the disease do not apply vaccination (eg, USA, Canada, and Europe).
What is a vesicular rash?
A vesicle is a small, fluid-filled blister. It can range in size from pinpoint to 5 millimeters, which is about the size of a pencil eraser. A vesicular rash occurs when there are vesicles in the area of your rash.
How long does hog cholera last?
Pigs develop protective immunity one week to ten days after vaccination and the immunity lasts two to three years (i.e. the lifetime of many sows and boars).
How is SVD being transmitted?
Mode of transmission
SVD is normally transmitted directly from pig to pig and affects only pigs, being shed in vesicle fluid and in the faeces. The virus enters by the oronasal route, usually through the tonsil, and also through the skin of the head, tongue, the foot especially of the coronary band, and via the gut.
Is there a vaccine for vesicular stomatitis?
A single dose of a vesicular stomatitis virus-based influenza vaccine confers rapid protection against H5 viruses from different clades | npj Vaccines.
What pathogen causes vesicular stomatitis?
Vesicular stomatitis can be caused by four named viruses in the genus Vesiculovirus (family Rhabdoviridae): vesicular stomatitis New Jersey virus (VSV-NJ), vesicular stomatitis Indiana virus (VSV-IN), vesicular stomatitis Alagoas virus (VSV- AV) and Cocal virus.
Is stomatitis contagious to humans?
Aphthous stomatitis is not contagious. You may be able to prevent or reduce your risk for canker sores through lifestyle changes. You may not need medical treatment for canker sores.
What does VSV infect?
Vesicular stomatitis is a viral disease which primarily affects horses, cattle, and swine. The agent that causes vesicular stomatitis, VSV, has a wide host range and can occasionally infect sheep and goats.
What kind of virus is VSV?
VSV is a zoonotic arbovirus that belongs to the family, Rhabdoviridae, the same family as the rabies viruses. VSV has an 11 kb genome that consists of a single strand of negative-sense RNA.