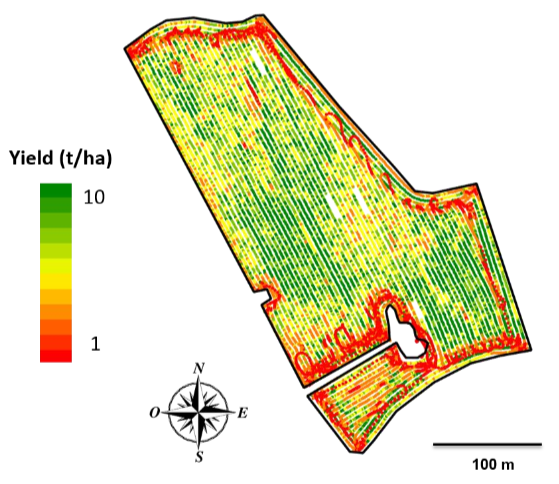
How does yield mapping work?
Yield mapping refers to the process of collecting georeferenced data on crop yield and characteristics, such as moisture content, while the crop is being harvested. Various methods, using a range of sensors, have been developed for mapping crop yields.
What is yield mapping in agriculture?
Confident yield mapping at harvest enables effective analysis and review of the season, including evaluation of any variable rate management strategies and on-farm trials. The challenge is capturing good quality data, reliably, which can later be used with confidence in your precision agriculture plan.
What is yield monitoring and mapping?
Yield mapping or yield monitoring is a technique in agriculture of using GPS data to analyze variables such as crop yield and moisture content in a given field. … This data produces a yield map that can be used to compare yield distribution within the field from year to year.
Is a farming management concept based on observing measuring and responding to inter and intra field variability in crops?
Precision agriculture (PA) is a farming management concept based on observing, measuring and responding to inter and intra-field variability in crops. … The practice of precision agriculture has been enabled by the advent of GPS and GNSS.
How does a combine measure yield?
The two halves of the bracket are held together by flexible strips which allow some movement as the grain hits a deflection plate. The harder the grain hits this plate the more the resistance of the potentiometer changes. This change is converted to an electronic signal which can be used to calculate yield.
What is Ag Leader?
Ag Leader Technology, based in Ames, Iowa, has been a front-runner and driving force behind precision agriculture innovation since 1992. Ag Leader’s products are the most complete, user-friendly package of precision farming technologies.
What are the basic components of a yield monitor?
Yield Monitor Systems
Yield monitors are a combination of several compo- nents (Figure 1). They typically include a data stor- age device, user interface (display and key pad), and a console located in the combine cab, which controls the integration and interaction of these components.
What is auto guidance system?
Auto guidance, a technology that pilots farm machinery via GPS satellites, could help farmers boost productivity and expand their farm operations. … More advanced auto-guidance options possess similar capabilities with an additional option to automatically guide the vehicle.
What is the use of remote sensing satellites?
Remote sensing is the process of detecting and monitoring the physical characteristics of an area by measuring its reflected and emitted radiation at a distance (typically from satellite or aircraft). Special cameras collect remotely sensed images, which help researchers “sense” things about the Earth.
What is crop discrimination and yield monitoring?
Remote sensing technology is used for crop discrimination. … • Crop discrimination types using remote sensing techniques (tools and technology) are based on the characterization and understanding of the electromagnetic behavior of target (Wavelength).
What do you know about crop simulation models?
A Crop Simulation Model (CSM) is a simulation model that describes processes of crop growth and development as a function of weather conditions, soil conditions, and crop management. … They are dynamic models that attempt to use fundamental mechanisms of plant and soil processes to simulate crop growth and development.
Which indices can be used as potential variables for crop discrimination?
Vegetation indices are used as potential variables for crop type discrimination.
What are the benefits of yield mapping?
Yield mapping lets farmers pick better combinations, and even get to know which hybrid does well in which type of soil and which one does not succeed. For this reason, you can raise more food for everyone after the end of the season.
How is geospatial technology used in agriculture?
Because crops are location-based, this makes Geographic Information Systems (GIS) an EXTREMELY relevant tool for farmers. For example, farmers use precision GPS on the field to save fertilizer. Also, satellites and drones collect vegetation, topography, and weather information from the sky.
What are the 3 geospatial technologies used in agriculture?
Farmers can use geospatial technologies such as GPS, GIS, and Landsat satellite imagery to assess variations in soil quality for planting crops.
What is Farm scouting?
Crop scouting, also known as field scouting, is the very basic action of traveling through a crop field while making frequent stops for observations. Crop scouting is done so that a farmer can see how different areas of his or her field are growing.
What is geospatial technology PPT?
The term geospatial technology (GST) refers to geographical information systems (GIS), global positioning systems (GPS), and remote sensing (RS), all emerging technologies that assist the user in the collection, analysis, and interpretation of spatial data.
What is satellite imagery in agriculture?
Satellite monitoring of the crops allows tracking of the positive and negative changes in the crop development using high resolution satellite images. … Such monitoring technology lets farmers monitor crops in different areas, fields, regions, and countries.
How does variable rate technology work?
Variable-rate technology (VRT) allows fertiliser, chemicals, lime, gypsum, irrigation water and other farm inputs to be applied at different rates across a field, without manually changing rate settings on equipment or having to make multiple passes over an area.
How much does a crop scout make?
Crop Scouts in America make an average salary of $34,276 per year or $16 per hour. The top 10 percent makes over $79,000 per year, while the bottom 10 percent under $14,000 per year.
How often should you scout for pests?
Tip #6: Scout Frequently
Frequent scouting provides the opportunity to detect and address problems before damage occurs. Therefore, we recommend scouting at minimum once per week and more often when conditions are favorable for problem pests.
How do you monitor crop yield?
Yield Monitoring in Precision Agriculture
Yield monitors work in three very simple steps: the grain is harvested and fed into the grain elevator which has sensors that read moisture content of the grain. After that process as the grain is being delivered to the holding tank, more sensors monitor the grain yield.
Where do mapping errors occur the most in yield and planting maps?
These errors most commonly appear in yield maps as straight lines down a pass or in fields with point-rows. One needs to either adjust the harvest width for these points or remove from the map before analyses.
What are the disadvantages of precision farming?
- High capital costs may discourage farmers to not adopt this method of farming.
- Precision agriculture techniques are still under development and requires expert advice before actual implementation.
Why is soil mapping important?
Soil mapping provides important information about the characteristics and condition of the land. There are generally two levels to a soil map for land use management. The first is an inventory of soil properties, which by themselves describe the condition of the soils when they were mapped.
What is Nano fertilizer?
A nanofertilizer is any product that is made with nanoparticles or uses nanotechnology to improve nutrient efficiency. … The use of nanotechnology for fertilizers is still in its infancy but is already adopted for medical and engineering applications.
What is crop discrimination?
Crop discrimination is a necessary step for most agricultural monitoring systems. Radar polarimetric responses from various crops strongly relate to the types and orientations of the local scatterers, which makes the discrimination still difficult using the polarimetric synthetic aperture radar (PolSAR) technique.
What is variable rate seeding?
Variable-rate seeding (VRS) is a precision agricultural technology that can properly and accurately adjust the seeding rate according to factors such as soil nutrients, light, and water storage capacity, which can not only greatly increase the crop yield, but also reduce the amount of seed used.
How can we improve crop yields?
- Quality Of Seeds. Agricultural productivity depends on the quality of seeds with which farmers sow their fields. …
- Field Productivity Zoning. …
- Monitoring Crops Growth. …
- Accurate Weather Prediction. …
- Regular Scouting. …
- Crop Protection Methods. …
- Soil Testing & Its Quality.
What are the two key methods of use of variable rate technology?
There are two key methods of use: sensor-based VRT and map-based VRT. Sensor-based VRT uses crop sensors in order to determine what materials, and how much of each, is necessary to optimise crop growth.
What is the use of yield monitoring?
A yield monitor is used to measure grain flow as it is deposited in the grain tank. Each second or two, while harvesting the crop, the harvester’s position in the paddock and the grain flow are recorded in the data logger. Some units can record information on weed levels in crops.
What is done to get good yields?
Plant Early, Plant Effectively
The best strategy to use to increase yields is: if your soil is ready, start planting. There are tests you can perform on your soil to see if it is ready for planting. … Planting early can result in increased yields by taking advantage of unexpectedly early favorable soil conditions.
How does yield mapping work?
How Does Grain Yield Mapping Work? Grain yield mapping works simply: as the combine passes over the field, the system collects georeferenced data of the crop yield using a range of sensors and creates a yield map. Grain flow sensors measure the amount of grain harvested by a combine in a unit of time.
Which technique helps in achieving high yield in crops?
The three methods to increase the yield of crops are: Using high yielding variety seeds. Use of modern irrigation methods so as to obtain more amount of water. Crop rotation so as to increase the fertility of the soil.
Why is yield data important?
Yield monitor data is certainly one of the most valuable pieces of information that is gathered throughout the year. It can allow producers to estimate profitability, evaluate management decisions, and develop recommendations for the upcoming year.
What is crop mapping?
Crop Mapping. Page 1. Maps of crop area, type and stage of development are used by many institutes, such as national agricultural agencies, regional agricultural bodies, statistical offices, NGO’s, etc., to estimate crop inventories of what, where, and when certain crops are grown.
Why is it important for farmers to look at previous year’s Farm Information and yield maps?
Yield Monitor Mapping
A zone-classified yield map is especially useful to farmers because it shows that yields vary throughout the field, such as where yields are high, low and in between, without the clutter of individual dots that vary widely in value.
What are the components of precision farming?
Generally, three major components of precision agriculture are information, technology, and management. Base on these three principles, we can define PA in different ways.
How can GIS help in precision agriculture?
GIS is used in precision agriculture to manage spatial information and help farmers make decisions. … The value of using GIS to record and analyse this information is that you can keep records over time and compare multiple variables (for example, soils, yield and elevation) to create management zones.